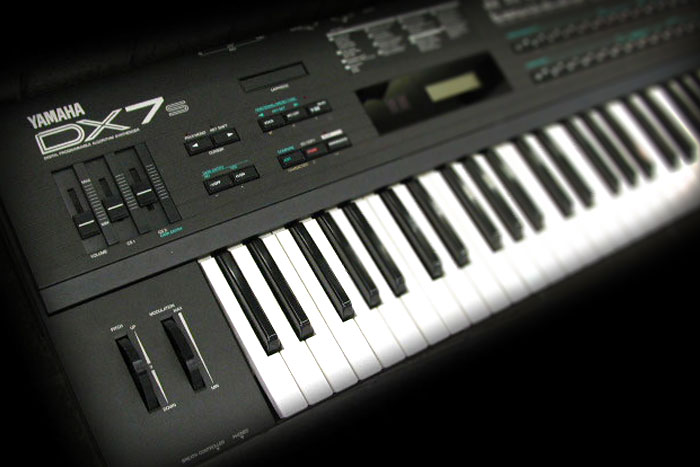
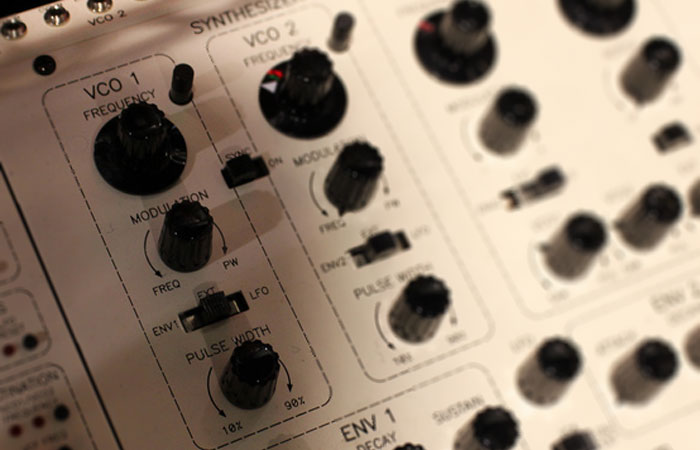
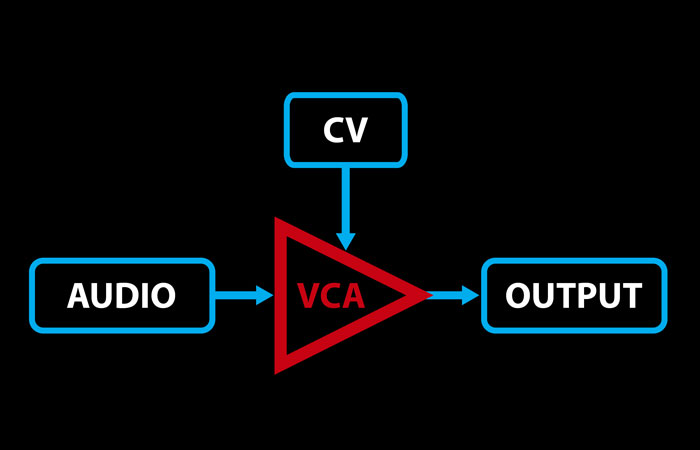
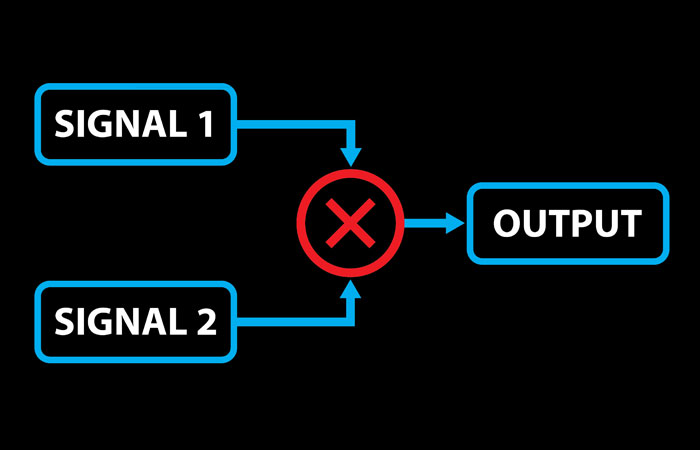
Frequency-Modulation Synthesis, or FM Synthesis for short, works differently than what we’ve talked about so far. It uses one wave to rapidly increase or decrease (modulate) the frequency of another, which creates entirely new frequencies that aren’t part of the first two. Don’t worry if that’s not very intuitive; I’m going to break it down […]


 Posted in
Posted in